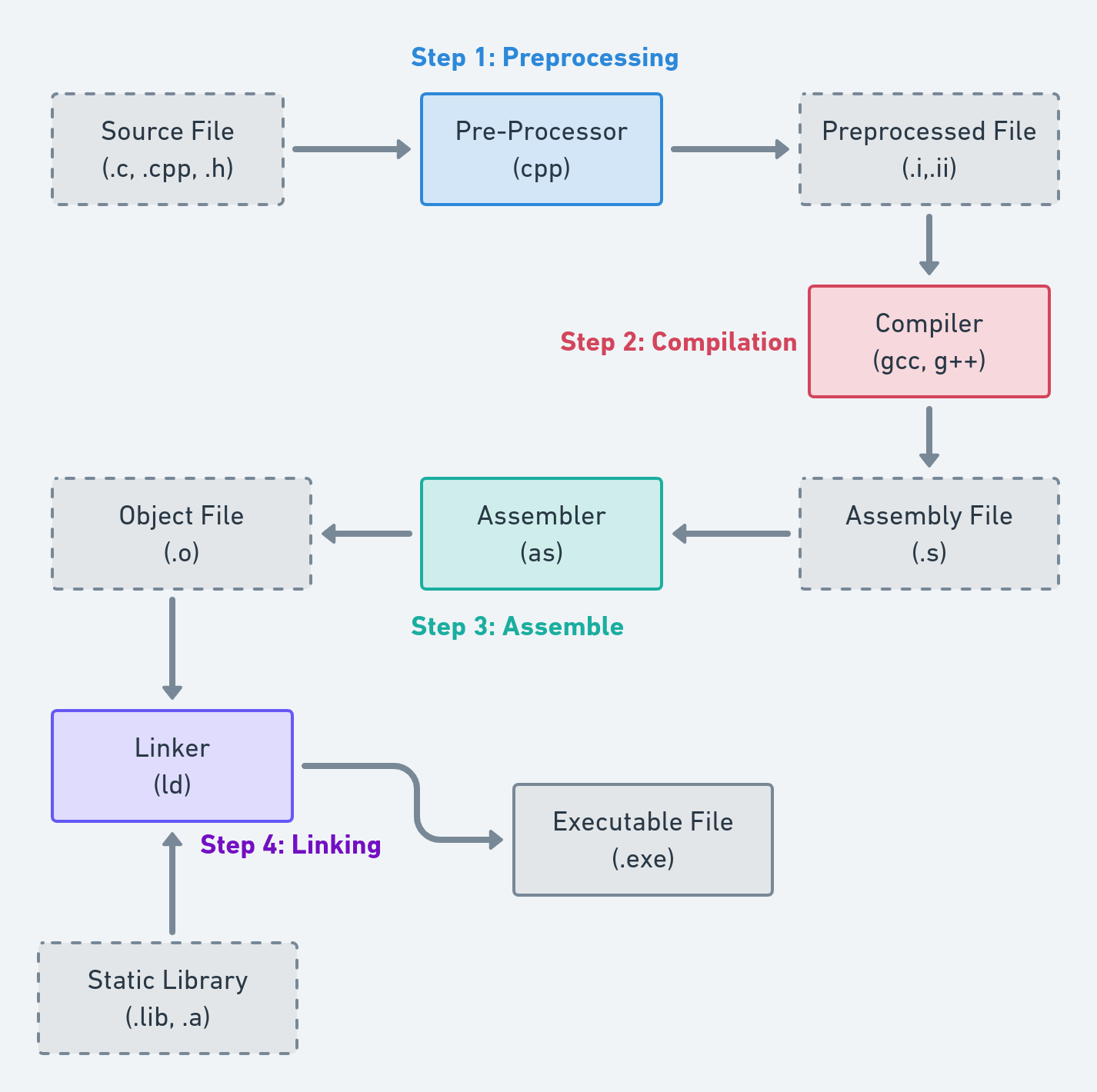
Steps of C++ codes compilation
g++ vs gcc
- g++ can compile any .c or .cpp files but they will be treated as C++ files only
- gcc can compile any .c or .cpp files but they will be treated as C and C++ respectively
- Using g++ to link the object files, files automatically links in the std C++ libraries. gcc does not do this.
Compilation
Suppose we have simplest code in main.cpp file, then
1 | g++ main.cpp # Produces the executable file (with default name i.e a.out) |
Not a Single Step Process!
- Word Compilation is using wrongly.
- Compilation is just Step 2 of the complete pipeline below.
Barebone Source file
1 |
|
Step 1: Preprocessing
g++ -E main.cpp
Outputs:
1 | # 1 "main.cpp" |
Step 2: Compilation
g++ -S main.cpp
Outputs: main.s
1 | .file "main.cpp" |
Step 3: Assemble
g++ -c main.cpp
Outputs: main.o
It’s a binary file, so we cannot read it.
Step 4: Linking
g++ main.cpp
Outputs: a.out which is executable.
Using Multiple files
Take following 3 files:
1 | // main.cpp |
1 | g++ main.cpp add.cpp -o main # Generates executable file 'main' which outputs 5 when executed |