ML model visualization using Netron
1. Intro
- Netron is really great tool to visualize the ML models.
- ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange Format) is a format designed to represent any type of Machine Learning and Deep Learning models.
- Pytorch and Tensorflow can export the model in onnx format.
- This onnx file can then be read with Netron to visualize the model graphically.
2. Installation
As simple as:
1 | pip install netron |
3. Barebone code
1 | import torch |
Output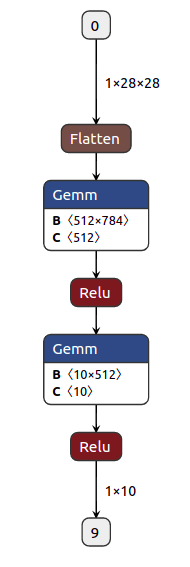
- Above code will open the visualization in browser @
http://localhost:8080/ - It needs a dummy input to pass through the model and calculate necessary data.
- Dummy input can be anything. It just needs to have right shape that model takes.
- To name the inputs and outputs, add following parameters to the
torch.onnx.exportfunction.
1 | torch.onnx.export(model, dummy_input, model_path, |
4. Show tensor shapes at each step
- Install
onnxpackage1
pip install onnx
- After exporting the onnx file, read back using
onnx.loadand then infer the tensor shapes1
2
3
4# Input tensor shapes at each step
onnx.save(onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx.load(model_path)), model_path)
netron.start(model_path) # Visualize using Netron
Output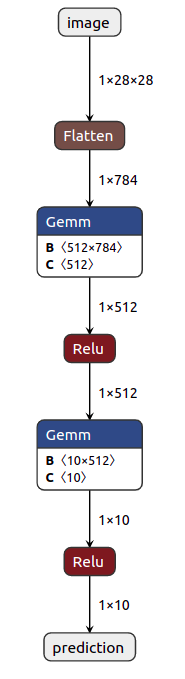
- This is a lot better visualization of model
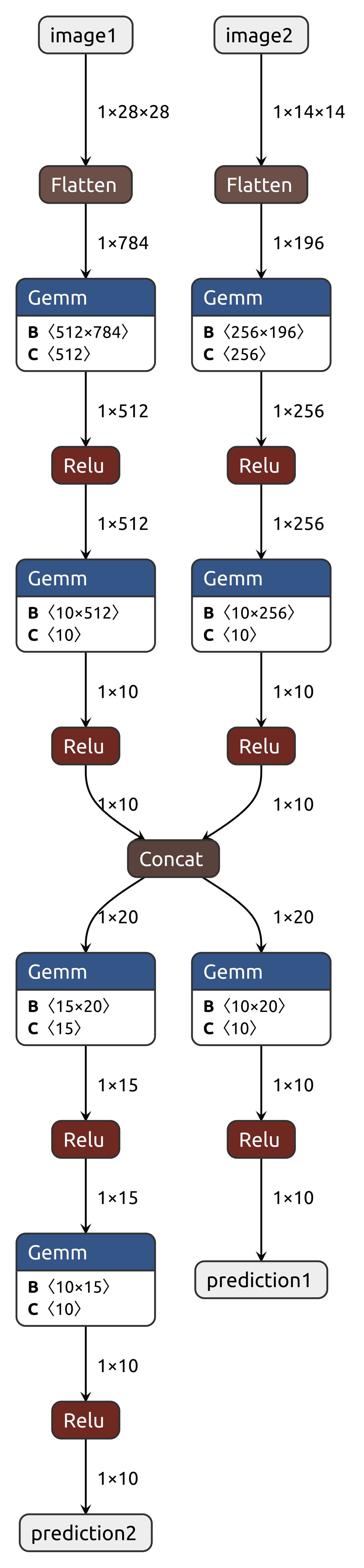
5. Multiple Inputs Outputs
- Here is example using Two inputs and Two outputs
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import netron
import onnx
# Define the Model
class NeuralNetwork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(NeuralNetwork, self).__init__()
self.flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.dense1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(28*28, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(512, 10),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.dense2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(14*14, 256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(256, 10),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.head1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(20,10),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.head2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(20,15),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(15,10),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x, y):
x_out = self.flatten(x)
y_out = self.flatten(y)
x_out = self.dense1(x_out)
y_out = self.dense2(y_out)
combined = torch.cat((x_out,y_out),1)
pred1 = self.head1(combined)
pred2 = self.head2(combined)
return pred1, pred2
model = NeuralNetwork() # Create a Model
dummy_input1 = torch.ones([1,28,28]) # Dummy Input (batch_size=1, input_shape=(28x28))
dummy_input2 = torch.ones([1,14,14]) # Dummy Input (batch_size=1, input_shape=(14x14))
model_path = "simple_model.onnx" # Path of the onnx file
torch.onnx.export(model, (dummy_input1, dummy_input2), model_path,
input_names = ['image1', 'image2'],
output_names = ['prediction1', 'prediction2']) # Export the model to ONNX file
# Input tensor shapes at each step
onnx.save(onnx.shape_inference.infer_shapes(onnx.load(model_path)), model_path)
netron.start(model_path) # Visualize using Netron
Output